In Prokaryotes the Rna Polymerase Holoenzyme Consists of
Initiation of transcription is a primary means for controlling gene expression. Holoenzyme is also known as a conjugate enzyme.
Solved In Prokaryotes The Rna Polymerase Holoenzyme Is Chegg Com
Catalysis derives from the β and β subunits.

. In prokaryotes the RNA polymerase holoenzyme consists of Both the location of the start site and the direction of transcription can be established. Holoenzyme contains all the subunits required for the functioning of an enzyme eg. Two alpha subunits two beta subunits and two.
2 form the core enzyme-The core enzyme plus form the holoenzyme-The promoter in prokaryotes has conserved sequences at -35 at -10 and has the transcription start site at 1. The core polymerase plus two alpha subunits b. The prokaryotic polymerase consists of a core enzyme of four protein subunits and a σ protein that assists only with initiation.
It consists of RNA polymerase II a subset of general transcription factors and regulatory proteins known as SRB proteins. The core polymerase plus two beta subunits. 18S and 28S rRNA synthesis.
-The nascent RNA that is synthesized by the RNA. We have determined crystal structures refined to 414 Å-resolution of RPo containing Thermus aquaticus RNAP holoenzyme and. The RNA polymerase II transcription machinery consists of over 50 proteins which are thought to bind to the core promoter in as few as two steps.
Elongation synthesizes mRNA in the 5 to 3 direction at a rate of 40 nucleotides per second. In prokaryotes the RNA polymerase holoenzyme consists of a. The core polymerase plus a sigma subunit e.
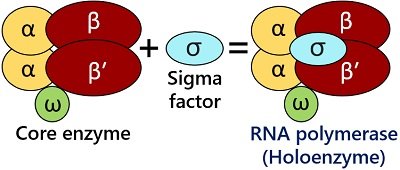
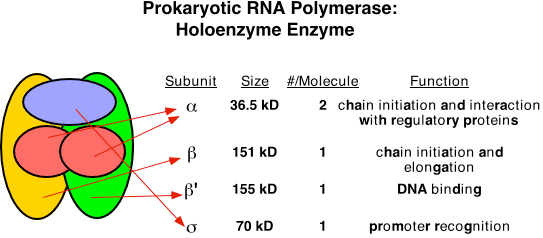
DNA polymerase III RNA polymerase. In bacteria the RNA polymerase RNAP holoenzyme binds and unwinds promoter DNA forming the transcription bubble of the open promoter complex RPo. The Escherichia coliRNA polymerase RNAP is a multi-subunit enzyme composed of five subunits including α two copies β β and ω subunits.
TATAAT located 10 nt upstream from the start site and TTGACA located 35 nt upstream from the start site. Holoenzyme Apoenzyme Cofactor. Termination liberates the mRNA and occurs either by rho protein interaction or by the formation of an mRNA hairpin.
Binding of TFIIA-TFIID followed by binding of a large pre-assembled holoenzyme complex consisting of the remaining GTFs RNA polymerase II and associated regulatory proteins. The RNAP holoenzyme in bacteria consists of five subunits. The two α subunits and the ω subunit function to assemble the enzyme and bind to the DNA sequence to be transcribed.
Coli the polymerase is composed of five polypeptide subunits. These subunits have been found to have similar functions structures and sequences to specific subunits of eukaryotic polymerase II. -RNA polymerase consists of the following proteins.
It consists of RNA polymerase II a subset of general transcription factors and regulatory proteins known as SRB proteins. Aloysius College Autonomous Jabalpur MP. In bacteria the binding of a single protein the initiation factor σ to a multi-subunit RNA polymerase core enzyme results in the formation of.
Holoenzyme is a complete functional enzyme which is catalytically active. This complex can be recruited more Transcription by RNA Polymerases I and III. The catalytic core subunit α2ββῳ is evolutionary conserved in its structure and function since RNAp is almost.
The core polymerase plus two beta subunits c. CTD C-terminal domain The. Part of the assembly of the holoenzyme is referred to as the preinitiation complex because its assembly takes place on the gene promoter before the initiation of.
The RNA molecule is synthesized between the β and β subunits. Tion Nitin Swamy Department of Biotechnology St. The holoenzyme consists of a preformed complex of RNA polymerase II the general transcription factors TFIIB TFIIE TFIIF and TFIIH and several other proteins that activate transcription.
Coli the RNA polymerase core enzyme is composed of five protein subunits α 1 α 2 β β and ω see figure 94. Two 6-base sequences are present in bacterial promoters. Prokaryotes use the same RNA polymerase to transcribe all of their genes.
Core enzyme of RNA polymerase containing four polypeptides twoαoneβand oneβ. RNA Polymerase Holoenzyme Consists of the Core Enzyme and then the Sigma Factor Bacterial RNA polymerase can be divided into the α2ββω core enzyme that catalyzes transcription and the σ subunit that is required only for initiation. RNA Polymerase is the enzyme that produces the mRNA molecule just like DNA polymerase produced a new DNA molecule during DNA replication.
Holoenzyme consists of an apoenzyme together with its cofactors. RNA polymerase -1 transcribes eukaryotic ribosome which does not consists of A. 383 Accesses 31 Citations Metrics Abstract BACTERIAL RNA polymerase consists of a core α2ββ and a sigma σ factor which form the active holoenzyme.
Transcription initiation requires the RNA polymerase holoenzyme to bind to the promoter DNA sequence. RNA polymerase I It helps in the. Part of the assembly of the holoenzyme is referred to as the preinitiation complex because its assembly takes place on the gene.
RNA polymerase holoenzyme Background Transcription in all cellular organisms is driven by a complex multi- subunit and multi- functional enzyme the DNA dependent RNA polymerase RNAp. The core polymerase plus a sigma subunit. Bacterial RNAp consists of five subunits.
Alpha alpha prime beta beta prime and omega11. These subunits assemble every time a gene is transcribed and they. The core polymerase plus two alpha subunits two beta subunits and a sigma subunit.
These five subunits form the RNAP core enzyme responsible for RNA synthesis using DNA as. RNA polymerase III It helps in the synthesis of the tRNA ScRNA rRNA and snRNA small nuclear RNA. Two alpha subunits two beta subunits and two sigma subunits.
In prokaryotes the RNA polymerase holoenzyme consists of Multiple Choice the core polymerase plus two alpha subunits. RNA polymerase II It helps in the synthesis of the HnRNA heterogeneous nuclear RNA and mRNA. The core polymerase plus two alpha subunits two betas subunits and a sigma subunit d.
What Is Bacterial Transcription Definition Key Terms Steps Biology Reader

No comments for "In Prokaryotes the Rna Polymerase Holoenzyme Consists of"
Post a Comment